Graphene quantum dots
|
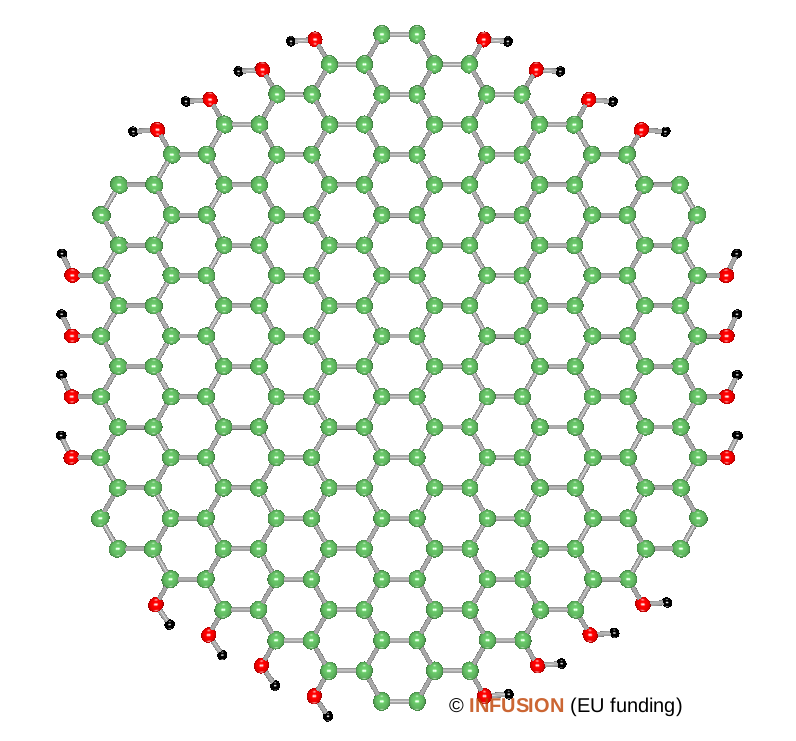
A quantum dot is a nanostructure having small dimensions in the three directions of space. According to this definition, a graphene quantum dot (GQD) is a small piece of monolayer or few layer graphene. The diameter is typically below 20~nm. GQDs can be produced by a large variety of methods, either bottom-up or top-down [1]. Top-down methods consist in transforming a macroscopic carbon precursor into nanomaterials. Green chemistry approaches use natural precursors for that, for instance leaves or fruits. Defects are present, especially in the case of a top-down production. Very often, groups such as OH, COOH ... are attached on the edges atoms. Like with reduced graphene oxide, C-O-C epoxide rings may exist on the surface together with other defects. The GQDs can combine several interesting properties: photoluminescence, photostability, good dispersibility in aqueous and organic solvents, biocompatibility, large absorption coefficient for infrared, visible and UV radiations. The luminescence spectrum depends on the size and composition of the quantum dots. Depending on the preparation method, GQDs can emit light in all colors of the visible spectrum when excited by UV radiations [2]. The figure represent an ideal graphene quantum dot of 2.8 nm diameter whose zigzag edges are decorated with OH groups. |
 |
- "Graphene quantum dots synthesis and energy application: a review" S.A. Prabhu, V. Kavithayeni, R. Suganthy, and & K. Geetha, Carbon Lett. 31 (2021) 1-12 [DOI: 10.1007/s42823-020-00154-w].
- "Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of functionalized graphene quantum dots with diverse fluorescence characteristics" V.A. Chhabra, R. Kaur, N. Kumar, A. Deep, C. Rajesh, and K.H. Kim, RSC Adv. 8 (2018) 11446-11454 [DOI: 10.1039/C8RA01148F].