Atomic force microscope
|
The atomic force microscope (AFM) is a very versatile instrument in nanotechnology. Like in the scanning tunneling microscope, an AFM contains a sharp tip whose position relative to the sample can be controlled with very high precision in three diction's. The tip is mounted at the end of a micro-fabricated cantilever that can bend as the result of forces that acts on the tip. The bending is monitored by an optical laser beam that amplifies the nanoscopic deflection of the cantilever. AFM offers many modes, as described with some details here. In contact mode, the tip is always in contact with the surface. During the scan, the vertical position of the sample is constantly adjusted so as to keep constant the deflection of the probe. The information is the two-dimensional map of the vertical displacement. |
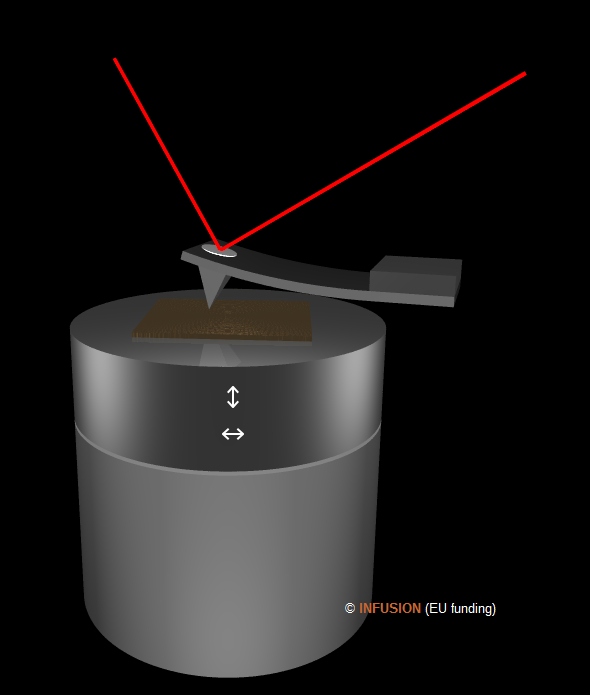 |
A more gentle way to probe the surface topography is the tapping mode. Here the cantilever (silicon) is forced to oscillate at or near its natural resonant frequency. The amplitude depends on the local tip--sample interactions in addition of course to the mechanical properties of the probe. During a scan, the average tip--sample distance varies due to variations of the sample topography under the tip. To keep the probe's vibration amplitude constant, the vertical position of the sample is constantly adjusted, which is traduced in a topographic signal while scanning the surface.
In the lift mode, a previously acquired topographic data is complemented by a new scan operated at a higher height to provide an additional information generated by attractive forces between tip and sample. The lift mode is used in Magnetic Force Microscopy (MFM) to visualize magnetic domains using a special magnetic tip (e.g. cobalt-chromium coated probe). The same principle applies in Electrostatic Force Microscopy (EFM) which collects information on the local electric field using a conducting tip (e.g. platinum-iridium coated probe). A Surface Potential Microscope (SPoM), or Kelvin nanoprobe, is also equipped with a conducting tip. During a lift-mode scan, the local contact potential difference between tip and sample is mapped.
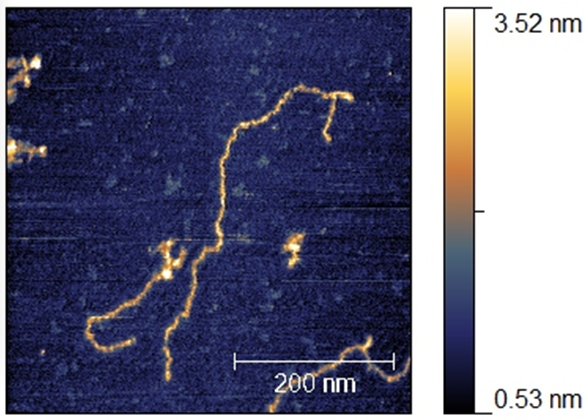 |
AFM image of DNA molecules deposited on mica (obtained with an A100-AFM of A.P.E. Research S.R.L.). |