Fullerenes
Fullerenes are cage-like polyciclic molecule composed exclusively of C atoms. Each atom is bound to three atoms by sigma bonds, like in graphene. The closing of the structure is realized by 12 pentagonal rings dispersed among hexagonal rings. It is taken as a rule that the most stable fullerenes are polyhedra in which the pentagons are surrounded by hexagons. The smallest and also the most symmetrical molecule that satisfies this rule is C60. Irrespective of the isolated pentagonal rule, a fullerene is composed of an even number N of atoms, with N ≥ 20, and the number of bonds is 3N/2. If the polyhedron defined by the N atoms is convex, it has 2+N/2 faces.
| Property | C60 | C70 |
|---|---|---|
| First ionization energy (eV) | 7.6 | 7.5 |
| Electron affinity (eV) | 2.7 | 2.8 |
| HOMO-LUMO gap (eV) | 2.3 | 2.2 |
| First optical transition (eV) | 3.76 | 2.63 |
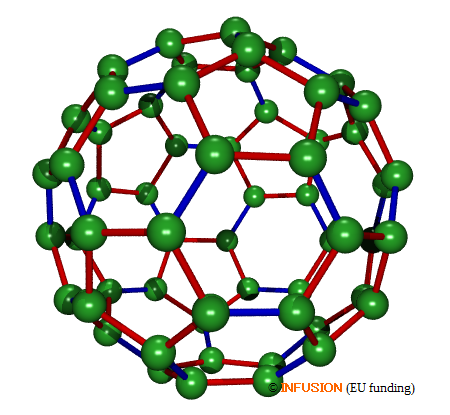 |
C60 has the shape of a truncated icosahedron. It is composed of 60 carbon atoms located at the vertices of the polyhedron, 12 pentagons (in red) and 20 hexagons (alternating blue and red edges). The bonds represented in blue (6:6 ring bonds) are slightly shorter than the bonds represented in red. The sphere circumscribed to the 60 vertices has a diameter of 0.71 nm. |